Influence of peer learning, self-regulatory learning, and mathematics interest on mathematics performance
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.33830/ijdmde.v2i1.10313Keywords:
peer learning, self-regulatory learning, mathematics interest, mathematics performanceAbstract
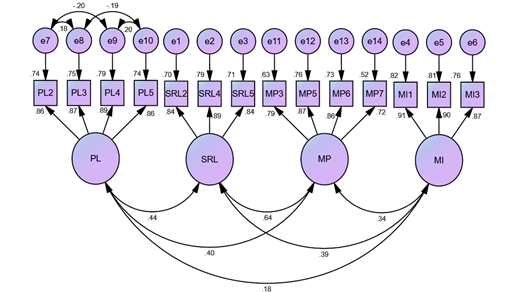
The current study examined the influence of peer learning, self-regulatory learning, and mathematics interest on mathematics performance. The study adopted descriptive survey using questionnaire for the data collection. 320 students were sampled from a total population of 1600 students using stratified sampling and simple random sampling techniques. The data collected was analysed using Structural equation modeling to examined the hypothesized paths. Based on the data analysis, peer learning, self-regulatory learning, and mathematics interest had a direct positive and statistically significant impact on mathematics performance. The study explores the impact of peer learning, self-regulatory learning, and mathematics interest on students' performance, offering insights for effective instructional strategies and policy interventions. Finally, the study suggests incorporating structured peer-learning activities, self-regulatory learning strategies, engaging mathematical contexts, and professional development programs for teachers to enhance student autonomy and interest in mathematics.
References
Ahn, I., Chiu, M. M., & Patrick, H. (2021). Connecting teacher and student motivation: Student-perceived teacher need-supportive practices and student need satisfaction. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 64(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2021.101950
Al Mutawah, M. A., Thomas, R., & Khine, M. S. (2017). Investigation into self-regulation, engagement in learning mathematics and science and achievement among Bahrain International Electronic Journal of Mathematics Education, 12(3), 633-653. https://doi.org/10.29333/iejme/639
Arthur, Y., Asiedu-Addo, S., & Assuah, C. (2017). Teacher-student variables as predictor of students’ interest in mathematics: the use of stepwise multiple linear regression analysis. Asian Research Journal of Mathematics, 4(3), 1–11. https://doi.org/10.9734/arjom/2017/33544
Arthur, Y. D., Dogbe, C. S. K., & Asiedu-Addo, S. A. A. (2021). Modeling students’ mathematics achievement and performance through teaching quality: SERVQUAL perspective. Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education. https://doi.org/10.1108/JARHE-06-2021-0243
Arthur, Y. D., Dogbe, C. S. K., & Asiedu-Addo, S. K. (2022). Enhancing performance in mathematics through motivation, peer assisted learning, and teaching quality: The mediating role of student interest. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 18(2), em2072. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/11509
Asare, B., & Boateng, F. O. (2025). Self-awareness and self-regulatory learning as mediators between ChatGPT usage and pre-service mathematics teacher's self-efficacy. Journal of Pedagogical Research, 1-17. https://doi.org/10.33902/JPR.202530637
Asare, B., Arthur, Y. D., & Boateng, F. O. (2023). Exploring the impact of ChatGPT on mathematics performance: The influential role of student interest. Education Science and Management, 1(3), 158-168.
Asare, B., Welcome, N. B., & Arthur, Y. D. (2024). Investigating the impact of classroom management, teacher quality, and mathematics interest on mathematics achievement. Journal of Pedagogical Sociology and Psychology, 6(2), 30-46. https://doi.org/10.33902/jpsp.202426232
Bah, Y. M. (2022). Poor performance in mathematics among senior secondary school students: Lessons for education planners and parents. International Journal of Education and Learning, 4(1), 10–19. https://doi.org/10.31763/ijele.v4i1.605
Bamfo, B. Ab., Dogbe, C. S. K., & Mingle, H. (2018). Abusive customer behaviour and frontline employee turnover intentions in the banking industry: The mediating role of employee satisfaction. Cogent Business and Management, 5(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2018.1522753
Berger, N., Mackenzie, E., & Holmes, K. (2020). Positive attitudes towards mathematics and science are mutually beneficial for student achievement: a latent profile analysis of TIMSS 2015. In Australian Educational Researcher (Vol. 47, Issue 3). Springer Netherlands. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13384-020-00379-8
Boadu, S. K., Arthur, Y. D., & Bonyah, E. (2023). Mediation and moderation effects of motivation and teaching quality on the relationship between peer tutoring and mathematics achievement. Journal of Mathematics and Science Teacher, 3(2), em039. https://doi.org/10.29333/mathsciteacher/13166
Bright, A. N. B. W. Y. D. A., Welcome, N. B., & Arthur, Y. D. (2024). The effect of using technology in teaching and learning mathematics on student’s mathematics performance: The mediation effect of students’ mathematics interest. Journal of Mathematics and Science Teacher, 4(2), 14309.
Chatzistamatiou, M., & Dermitzaki, I. (2013). Teaching mathematics with self- regulation and for self-regulation : teachers’ reports. Hellenic Journal of Psychology, 10, 253–274.
Chand, S., Chaudhary, K., Prasad, A., & Chand, V. (2021). Perceived causes of students’ poor performance in mathematics: a case study at ba and tavua secondary schools. Frontiers in Applied Mathematics and Statistics, 7(April), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fams.2021.614408
Dogbe, C. S. K., Tian, H. Y., Pomegbe, W. W. K., Sarsah, S. A. T. O., & Otoo, C. O. A. (2020). Market orientation and new product superiority among small and medium-sized enterprises (smes): The moderating role of innovation capability. International Journal of Innovation Management, 24(5). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1363919620500437
Draijer, J. M., Bakker, A., Slot, E., & Akkerman, S. (2020). The multidimensional structure of interest. Frontline Learning Research, 8(4), 18–36. https://doi.org/10.14786/flr.v8i4.577
Edo, H., Vivian, M., Asare, B., & Arthur, Y. D. (2024). Pre-service teachers' mathematics achievement, attitude, and anxiety: the moderative role of pre-service teachers' interest in the learning process. Pedagogical Research, 9(2), 1–10.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.2307/3151312
Hu, X., Gong, Y., Lai, C., & Leung, F. K. S. (2018). The relationship between ICT and student literacy in mathematics, reading, and science across 44 countries: A multilevel analysis. Computers and Education, 125(2), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2018.05.021
Jaffe, E. (2020). Mindset in the Classroom: Changing the Way Students See Themselves in Mathematics and Beyond. The Clearing House: A Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas, 93(5), 255–263. https://doi.org/10.1080/00098655.2020.1802215
Kirschner, P. A., Hendrick, C., Heal, J., & Caviglioli, O. (2022). Mathematical Knowledge for Teaching. In How Teaching Happens (Vol. 1, Issue July). https://doi.org/10.4324/9781003228165-21
Ko, W. H. (2018). The development of a competence scale of food safety and hygiene for hospitality students. Journal of Food Safety, 38(5), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfs.12498
Laine, E., Veermans, M., Gegenfurtner, A., & Veermans, K. (2020). Individual interest and learning in secondary school stem education. Frontline Learning Research, 8(2), 90–108. https://doi.org/10.14786/FLR.V8I2.461
Lim, C. L., Jaya, S., Jalil, H. A., & Saad, W. Z. (2023). Peer Learning , Self-Regulated Learning and Academic Achievement in Blended Learning Courses : A Structural Equation Modeling Approach. 110–125.
Liu, Y., Wang, Y., Liu, R. De, Ding, Y., Wang, J., & Mu, X. (2022). How Classroom Environment Influences Academic Enjoyment in Mathematics Among Chinese Middle School Students: Moderated Mediation Effect of Academic Self-Concept and Academic Achievement. Psychology Research and Behavior Management, 15(August), 2035–2048. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S371092
Miller, M., & Hadwin, A. (2015). Scripting and awareness tools for regulating collaborative learning: Changing the landscape of support in CSCL. Computers in Human Behavior, 52, 573–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.01.050
Moeyaert, M., Klingbeil, D. A., Rodabaugh, E., & Turan, M. (2021). Three-Level Meta-Analysis of Single-Case Data Regarding the Effects of Peer Tutoring on Academic and Social-Behavioral Outcomes for At-Risk Students and Students With Disabilities. Remedial and Special Education, 42(2), 94–106. https://doi.org/10.1177/0741932519855079
Moliner, L., & Alegre, F. (2022). Attitudes, beliefs and knowledge of mathematics teachers regarding peer tutoring. European Journal of Teacher Education, 45(1), 93–112. https://doi.org/10.1080/02619768.2020.1803271
Ms. S. Kalpana | Ms. V. A. Malathi. (2019). A study on interest in mathematics interest and its relation to academic achievement in mathematics among higher secondary students. International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development, 3(4), 1246–1254. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.31142/ijtsrd25113
Oduro, E. O. (2015). Assessment in mathematics classrooms in Ghana: a study of teachers' practices (Doctoral dissertation, University of Sussex).
Roscoe, R. D., & Chi, M. T. H. (2007). Understanding tutor learning: knowledge-building and knowledge-telling in peer tutors’ explanations and questions. Review of Educational Research, 77(4), 534–574. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654307309920
Salkind, N. (2012). Internal consistency reliability. Encyclopedia of Research Design. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781412961288.n191
Teoha, S. H., Koo, A. C., & Singh, P. (2010). Extracting factors for students’ motivation in studying mathematics. International Journal of Mathematical Education in Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207391003675190
Thurston, A., Roseth, C., Chiang, T.-H., Burns, V., & Topping, K. J. (2020). The influence of social relationships on outcomes in mathematics when using peer tutoring in elementary school. International Journal of Educational Research Open, 1(June), 100004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijedro.2020.100004
Trochim, M. K., & Donnelly, J. (2006). The Research Methods Knowledge Base, 2nd Edition. Atomic Dog Publishing, Cincinnati, OH., Internet WWW. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.05.029181
Tsuei, M. (2012). Using synchronous peer tutoring system to promote elementary students’ learning in mathematics. Computers and Education, 58(4), 1171–1182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2011.11.025
Yamane, I., & Sato, K. (1967). Effect of temperature on the decomposition of organic substances in flooded soil. Soil Science and Plant Nutrition, 13(4), 94–100. https://doi.org/10.1080/00380768.1967.10431981
Yazgı Yanık, Z., & Afat, N. (2022). Metacognitive awareness as a predictor of social emotional learning skills in gifted and talented students. Gifted and Talented International, 37(2), 109–118. https://doi.org/10.1080/15332276.2022.2053316
Yıldızlı, H., & Saban, A. (2016). The effect of self-regulated learning on sixth-grade turkish students’ mathematics achievements and motivational beliefs. Cogent Education, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2016.1212456
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Batsa Michael, Yarhands Dissou Arthur, Bright Asare

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.









